|
Developed Strategic Options to market their newly developed Catalyst for the Manufacture of Biodiesel from waste vegetable oils in the following Markets:
- Developed Strategic Options to market their newly developed Catalyst for the Manufacture of Biodiesel from waste vegetable oils in the following Markets:
- USA
- European Union
- India
- Selected Countries in Southeast Asia & Australia
-
Such a Strategy would be very successful in achieving the following Objectives:
- Wins the Argument conclusively "Food Versus Fuel" in the manufacture of biofuels
- In the EU if "Used Cooking Oil" is reused as the "feedstocks", companies secure double the "carbon or emission credit"
- It enables manufacturers to use lower-priced feedstocks and make biodiesel worth their while to manufacture
- There is plenty of waste vegetable oil or used cooking oil as it is called in the US and EU respectively, most of which is currently sent for dumping
2. DEVELOPED THE STRATEGIC OPTIONS FOR ONE OF THE TOP PRIVATE POWER GENERATING COMPANIES:
In India the Power Subsidiary of a Conglomerate had planned to put up a Power Project of 1,600 MW (supercritical coal plant) in Western India at a cost of US$2.50 billion in 2011. Tiara carried out this consulting assignment with great aplomb with the following outcome:
- This was the first Study carried out in India using the Quantitative Modeling techniques with Simulation Exercises including Monte Carlo Simulation.
- This showed the "Risk versus Reward" of all the Strategic Options.
- The initial reaction of the Company was that the power tariff (Rs. 3.80 per KWH) that Tiara recommended to them to quote to win power bids from the State Electricity Boards appeared to be very high and was very different from the tariff for another major power project (Mundra) that the Client was involved and in which they were in the final stages of commissioning the Plant
- While initially the Company was somewhat surprised with the recommendations, after some deep cogitation, they recognized its sterling importance and implemented the Study in its entirety.
The relevant "Principal Drivers Analysis" Diagram for one of the Strategic Options is shown by the Tornado Diagram as below:

The Risk Profiles of the Four Strategic Options are shown by the respective Curves below. The Probability of Destroying Shareholder Value (PDSHV) is given by the point of intersection of each Curve with the Y-Axis. It will be found that the Values are as below:
| 1. |
Strategic Option 1A |
52% |
|
| 2. |
Strategic Option 1C |
44% |
|
| 3. |
Strategic Option 2 |
46% |
|
| 4. |
Strategic Option 3 |
40% |
| 5. |
Strategic Option 4 |
43% |

The Risk Profiles of the Four Strategic Options are shown by the respective Curves below. The Probability of Destroying Shareholder Value (PDSHV) is given by the point of intersection of each Curve with the Y-Axis. It will be found that the Values are as below:
| 1. |
Strategic Option 1A |
52% |
|
| 2. |
Strategic Option 1C |
44% |
|
| 3. |
Strategic Option 2 |
46% |
|
| 4. |
Strategic Option 3 |
40% |
| 5. |
Strategic Option 4 |
43% |
3. Tiara's Assessment on Ultra Mega Power Plant (UMPP) in Western India for 4,000 MW involving Capital Investment of US$ 4 billion:
- Tiara pointed out that this project was unviable
- The power tariff in the region of Rs. 2.26 per KWH appears to be too low in the light of increased cost of procuring Indonesian Coal
- This is especially so when any tariff escalation can be done only for 40% of the imported coal as per the PPA
- There was a strong possibility that this project may turn out to be a non-performing Asset (NPA)
Unfortunately, all forecasts that Tiara made came true and the companies involved are still to get over these problems
- While Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC) appears to be willing to increase the power tariffs for the private companies, the State Electricity Boards are contesting this. Some of them have gone to Supreme Court
- As such the solutions that CERC came up with appear to be in temporary "stalemate"
4. ADVICE TO GOVERNMENT OF INDIA - MINISTRY OF POWER IN 2011/12:
Given below in the diagram Five Major Private Sector Competitors in Power Generation in India were compared as they related to the Power Tariffs and their relevant expected Rates of Return. Although, these were quoted successfully and projects won by the respective companies, they could not maintain the rates of return as the imported coal prices went up and in many cases there were no provisions in the Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) to increase the tariffs. Many of these power plants are losing heavily and have gone on appeal to the Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC) and the Ministry of Power (MoP), Government of India (GOI) to arbitrate in this matter.

- Highlighted to the Ministry of Power (MOP), Government of India (GOI) that the "bidding process" for their Ultra Mega Power Plants (UMPP) appeared to be untenable
- Even well-known companies preferred to underbid to win the business and then hoped to change Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) after a few years or even sooner if the cost of their procurement of feedstocks or any other commodity involved goes up significantly
- This was the problem faced by all companies involved in UMPP Projects such as the ones in Mundra (Gujarat), Krishnapatnam, (Andhra Pradesh) and others in several other states
- Tiara suggested alternative bidding process
- While GOI was very eager to let Tiara develop a new "bidding process", the conditions in India at that time were not favorable for Tiara to pursue this assignment
5. DIALOGUE WITH THE CENTRAL ELECTRICITY REGULATORY COMMISSION (CERC):
Tiara carried on a dialogue with CERC as it related to the "Bidding Process" for Ultra Mega Power Plants (UMPP) involving more than 4,000 MW each.
- Went over with CERC the Bidding Process in India for Power Projects and highlighted to them as to how it was flawed
- Went over with CERC the Bidding Process in India for Power Projects and highlighted to them as to how it was flawed
- Developing Scenario Planning for each variable
- Assigning Probabilities to each Scenario
- Assuming the right Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC)
- Developing a Principal Drivers Analysis
- Carrying out Simulation Exercises including Monte Carlo simulations
- Identifying the Risk Profile of the Project
- The Chairman, CERC was quite impressed and they even sent their Representatives to Tiara's Presentation the following day with ASSOCHAM
6. Special Sessions with Association of Chambers of Commerce and Industry (ASSOCHAM) in India:
- Made a Presentation on Tiara's Quantitative Modeling System (TQMS)
- Demonstrated as to how it provides for "out-of-the-box" thinking and Innovative Solutions
- Highlighted some of the Issues with Indian Companies as they related to "Intellectual Properties"
- Relevance of developing Strategic Options for each Project
- Identifying the Risk versus Reward of any project
- Illustrated all the above with an example of a Major Power Project in India
- Also highlighted what should be the role of GOI in this regard
- The Presentation was attended and participated by the Senior Members of CERC
- The President of ASSOCHAM was quite eager and wondering how to involve Tiara for many other GOI Projects such as 2G Spectrum when it came up for rebidding and other GOI major Capital Investment Projects
7. SYMPOSIUM IN NEW DELHI ON POWER IN AUGUST OF 2012:
- This was sponsored by the UK Group called "International Trades & Exhibitions", located in London, UK
- Participants, inter alia, included CERC, the Power Ministry, the Department of Atomic Energy, Coal Ministry, Department of New & Renewable Energy, Planning Commission, Independent Power Producers Association and so on
- Tiara made a Presentation on the "Strategic Issues of Power Generation"
- The response was very enthusiastic and there were recommendations from some of the delegates to the Seminar that Tiara should discuss further with MoP and also with CERC on Tiara's suggestions for future bidding on Major Power Projects
- There was general acceptance that when Power Companies bid for Projects they do not appear to be envisioning all possible scenarios while tendering their bids
8. INTERACTION WITH THE PLANNING COMMISSION, GOVERNMENT OF INDIA:
Met with the Senior Member of the Planning Commission (PC), who was former Cabinet Secretary of GOI with the following discussions:
- Made a Presentation of the outcome of a couple of Major Capex Projects in India which were originally approved by the Planning Commission (PC)
- PC has for its focus the following in their Capital Investment Projects:
- Deliver significant benefits to the communities for whom the project is intended
- Uses Resources of the Country quite optimally
- Provides benefits for the "Ahm Aadmee" (the Common Man)
- Provides benefits to the Investor or sponsoring company in the Private Sector
- It was pointed out that while many of the projects provide the benefits as per the first three bullets above, they do not usher in the benefits for the Private Investor
- As a matter of fact, Private Investors have done the bidding of many projects which after completion have turned out to be "Non-Performing Assets" (NPA)
- Tiara thereafter showed some examples where the Risk Profiles of the Projects showed the Probability of Destroying Shareholder Value as high as 80%
- It was therefore suggested to the Planning Commission that the "bidding process" should be such that GOI should not entertain projects where it is clear that the bidder will become a non-performing asset
- This does not mean that Companies may not come forward to bid but the economic environment should be such that the Private Sector is encouraged to bid for Projects
- This would call for some "new thinking" in developing in the first phase of Major Infrastructure Projects, which are generally sponsored either by the State Governments of GOI.
9. PRESENTATION TO ASSOCIATION OF POWER PRODUCERS (APP) IN INDIA:
- Met with the Director General of APP, who was former Additional Secretary of the Ministry of Power (MoP) in India
- While he appeared to be in favor Tiara making a Presentation to APP, he observed that MoP and GOI are involved in changing the "bidding process" for Ultra Mega Power Projects (UMPP), involving more than 4,000 MW of Power
- While he appeared to be in agreement the findings of Tiara in its Presentation, he pointed out that there were too many assumptions with too many variables involved
- It was then Tiara pointed out that whether the respective companies make their Viability Studies of Projects or Tiara does the same with their modeling, all of these are based on "Assumptions" as the Projects will materialize in a future whose economic and technological environment can at best be captured by "assumptions"
- Thereafter, he appeared to understand the wisdom of Tiara's Quantitative Modeling (TQM)
- It was felt by him that if Tiara could evaluate the new bidding process and thereafter make a Presentation with relevant assumptions of a new Model then it would be of use to the members of APP
10. DEVELOPMENT OF STRATEGIC OPTIONS FOR A MAJOR UREA PLANT USING NATURAL GAS IN GABON, WEST AFRICA WITH A CAPITAL INVESTMENT OF $3 BILLION:
One of the companies of a Conglomerate in India was approached by a Company in Southeast Asia to do a Joint Venture (JV) with them in a small West African Country for the manufacture and marketing of Urea. The country apparently has significant proven reserves of Natural Gas (NG) and the West African Country's Administration (WACA - more in the nature of a "dictatorship") was prepared to let the JV locate and pump the NG into their major manufacturing plant, where the hydrogen of NG will be made to coalesce and combine with the atmospheric nitrogen to produce ammonia which would then lead on to manufacturing Fertilizer of Urea Grade. In the first phase, they hoped to manufacture and market about 1.3 million tons of urea into various global markets. It appeared that as an inducement to make the JV invest into the country, provide the technology, export the product and develop overseas markets, the WACA was prepared to sell the natural gas at an extremely low price of $1 per million (MM) British Thermal Units (BTU) well below the world market prices of natural gas at that time around $4.50 per MMBTU.
The JV felt that they should be able to sell the urea in the world market. They had already made a series of assumptions and carried out economic evaluation of the project, which appeared to give the "go-signal" for the project. They had assumed some average price for selling the finished product of urea on a global basis. They were ready to go and sign their JV agreement when Tiara International Consulting (Tiara) was introduced to them. Tiara offered to carry out the "economic evaluation" of the project using their D&RA approach. The D&RA called for Pessimistic, Most Likely and Optimistic Estimates for each of the variables and they were eventually assumed as below. Incidentally, the "most likely" value was assumed as a "single-point" value by the JV which was extended further by Tiara using Pessimistic and Optimistic Values as under:
| INTERNATIONAL JV (IJV) - WEST AFRICAN COUNTRY ADMINISTRATION (WACA) |
PESSIMISTIC |
MOST LIKELY |
OPTIMISTIC |
| PROBABILITIES |
25% |
50% |
25% |
| CAPITAL INVESTMENT FOR PLANT & EQUIPMENT OUT OF THE ABOVE - 000'S US$ |
1,495,000 |
1,300,000 |
1,170,000 |
| COST OF NATURAL GAS AS PROVIDED BY WACA - US$ PER MMBTU | 2.00 | 0.80 | 0.80 |
| OTHER MARKETING COSTS AT US$/TON OF UREA | 0.00 | 10.00 | 5.00 |
| CAPACITY OF THE PLANT IN 000'S TONS | 1,087 | 1,359 | 1,427 |
| S-AMERICAN MKT PRICE AT DISTRBTR LEVEL -US$/TON | 250.00 | 275.00 | 300.00 |
| CENTR-AMCN MARKET PRICE AT DISTRIBTR LEVEL - $/TON | 255.00 | 275.00 | 300.00 |
| AFRICAN MKT PRICEAT DISTRIBUTOR LEVEL $/TON | 255.00 | 275.00 | 300.00 |
| AVERAGE MARKET DEMAND GROWTH RATE IN LATIN AMERICA | 0.89% | 1.79% | 2.68% |
| MARKET DEMAND GROWTH RATE IN CENTRAL AMERICA | 2.24% | 4.48% | 6.72% |
| MARKET DEMAND GROWTH RATE IN AFRICA | 1.87% | 3.75% | 5.62% |
| POTENTIAL MARKET SHARE - SOUTH AMERICA | 8.00% | 16.00% | 20.00% |
| POTENTIAL MARKET SHARE - CENTRAL AMERICA | 1.00% | 2.00% | 2.50% |
| POTENTIAL MARKET SHARE - AFRICA | 1.50% | 3.00% | 3.75% |
| WEIGHTED AVERAGE COST OF CAPITAL FOR THE JV - WACC | 8.50% | 8,50% | 8.50% |
| TIME TAKEN TO ACHIEVE FULL MARKET SHARE | 4.00 | 2.00 | 1.00 |
It appeared that the JV did not take into account the following risks
- Sovereign Risk: This is a "major risk" especially in a WACA, which is under the rule of a Dictator. Once the JV puts in their investment, technology and develops the global market in a few years, WACA may revert to them stating that $1 per MMBTU is too low a price for their only "raw material" in the country and people demand a much higher price, say world market price of $4.50 per MMBTU. This can completely destroy the project economics! Tiara felt that in all probability WACA would increase the price of NG by the third year of operation to at least $3.50 per MMBTU. Incidentally, such a situation occurred exactly three months after Tiara made the forecast in Oman where GOI had sponsored a JV with Omani Government. In 2014, Reliance is procuring a price of over $7.50 per MMBTU in the Indian Market.
- The other Sovereign Risk also involves "Nationalization" of the company as has happened in many countries in Africa, Asia and South America with expropriation of all company's assets.
- Obsolescing Bargain Risk: This is a risk that takes place with Private Sector Partners in any country. Once the loans are approved for a project using the global partner's name and the project is implemented, one of the influential private sector partners in the JV may gradually demand a higher share of equity and a greater role for themselves. While such a situation may not arise with the JV partner from Southeast Asia to the Conglomerate from India as the former already has majority equity, this has happened very frequently as observed by Tiara for many of the companies the latter has dealt with.
- Currency Risk: It is not clear what currency is used by the country in West Africa. Admittedly, for a project like this, all monetary issues are likely to be denominated in US Dollars or Euros. Nevertheless, it is useful to take cognizance of this in the final agreement with WACA
- Market Risk: The output of the project apparently will be sold in global markets. On investigation, it was found that the output could be sold in South and Central America as well as in the surrounding geographic markets to the West African Country. However, it was noticed that they did not have a marketing plan to show how much market shares would be achieved in each individual market, what the product pricing would be and what could go wrong in these markets. Further, the freight element for supplies to various markets was not taken into account.
All Other Risks: Some of these risks may not arise or can be of very minor in nature, but nevertheless worth taking into account as below:
- Risk towards Funds Repatriation
- Legal & Regulatory Risk
- Risk due To Corruption
- Operational Risk
- Labor Market Risk
- Intellectual Property Risk
- Supplier Risk
- Infrastructure Risk
- Political Stability Risk
- Security Risk
- Governmental Effectiveness Risk
- Risk Due To Tax Policies
Once someone assesses the above risks, then the person may wish to ignore many of these, which would not apply and concentrate only on the remaining ones which one endeavors to quantify. In this particular project, Tiara did not take them into account or quantify them as the JV was in a hurry to proceed with a D&RA.
A Quantitative Model was developed by Tiara taking into account whatever variables that could be quantified to include in the D&RA with their Pessimistic and Optimistic Values. The different sets of Scenarios assumed for the Model and the Results are shown in the Table hereunder:
- Scenario One: All assumptions are as per the Global JV without any increase in the price of NG, which was kept at the level of $1 per MMBTU for the entire 15 year project period with the average prices of Urea at (i) $300 per ton and then again at (ii) $275 per ton
- Scenario Two: All assumptions are as per Tiara without any increase in the price of NG, which was kept at the level of $1 per MMBTU for the entire 15 year project period with the average prices of Urea at (i) $300 per ton and then again at (ii) $275 per ton. Tiara's assumptions include "Freight" to global destinations and also some "Marketing Costs"
- Scenario Three: All assumptions are as per the Global JV with the price of NG increasing from $ 1 to $ 3.50 per MMBTU in 5th Year with the average prices of Urea at (i) $300 per ton and then again at (ii) $275 per ton
- All assumptions are as per Tiara with the price of NG increasing from $ 1 to $ 3.50 per MMBTU in 5th Year with the average prices of Urea at (i) $300 per ton and then again at (ii) $275 per ton. Again, Tiara's assumptions include "Freight" to global destinations and also some "Marketing Costs"
- Economic Evaluation and Results in the form of Economic Indicators for Scenarios 1 & 2 show significantly positive Net Present Values (NPVs) and as such we have not considered them in this write-up. However, economic results of Scenarios 3 & 4 involving Sovereign Risk show that except for one situation involving JV's assumptions with Urea price at $300 per ton, all other results show negative NPVs for the Project in what is described as the "Most Likely Scenario" as shown by the center column under the List of Assumptions.
- These have been tabulated and shown below. Some companies focus on NPVs while others pay special emphasis to IRRs & Payback Periods (nominal and real), while a few others look for Present Worth Payback Periods (PEPs - also known as Discounted Cash Flow Payback Periods) and Present Worth Index or PWI (the Bang for the Buck - given by the formula = NPV of Project Free Cash Flow/ (NPV of Project Free Cash Flow + NPV of max Cash Inflow). This PWI is frequently used by Investment Bankers and Venture Capitalists.
Economic Indicators for Scenarios involving Sovereign Risk
| ECONOMIC INDICATORS OF WEST AFRICA UREA PROJECT UNDER SOVREIGN RISK |
JV ASSUMPTIONS - UREA PRICE $300/TON |
TIARA ASSUMPTIONS - UREA PRICE $300/TON |
JV ASSUMPTIONS - UREA PRICE $275/TON |
TIARA ASSUMPTIONS - UREA PRICE $275/TON |
| NET PRESENT VALUE OF BUSINESS - MUS$ | 34,462 | (248,961) | (148,566) | (416,414) |
| NPV OF TERMINAL VALUE - MUS$ | 47,427 | 43,680 | 40,754 | 37,007 |
| DISCOUNTED CASH FLOW RATE OF RETURN - DCFROR OR IRR - NOMINAL | 10.91% | 7.82% | 8.69% | 5.82% |
| DISCOUNTED CASH FLOW RATE OF RETRUN - DCFROR OR IRR - REAL | 10.91% | 7.82% | 8.69% | 5.82% |
| SIMPLE PAYBACK PERIOD - NOMINAL - YEARS | 8.35 | 12.61 | 11.13 | 16.02 |
| SIMPLE PAYBACK PERIOD - REAL - YEARS | 8.35 | 12.61 | 11.13 | 16.02 |
| PRESENT WORTH PAYBACK PERIOD (PWP) - YEARS | 24.40 | - | - | - |
| PRESENT WORTH INDEX (PWI) -" the Bang for the Buck" | 1.05 | 0.69 | 0.80 | 0.50 |
"MUS$" means in 000's of US$ and "MMUS$" means in Millions of US$
The above is "Static" and not "Dynamic". All variables have been kept at "single point" value without varying them. Frequently, companies do Sensitivity Studies by changing "selected variables" and increase or decrease their values by say 10% and see the impact on the final outcome.
-
UNIQUENESS OF D&RA, WHERE IT ADDS VALUE TO THE ABOVE:
This is where "Decision & Risk Analysis" (D&RA) with Simulation Exercises differs significantly from the above. Future forecast of any assumption is considered a variable and the following is done for each one of the variables:
- Pessimistic and Optimistic Values are taken for each one
- Probability of occurrence for the "Most Likely" as well as the Pessimistic and Optimistic values is estimated, say at 25% for the "pessimistic", 50% for the "most likely" and 25% for the "optimistic" values
- Probability Distribution is given for each variable; it can be "Normal", "Log Normal", "Poisson", "Exponential", "Logarithmic" and so on. Here we have used "Normal Distribution".
- Thereafter, using a Special Software, Sensitivity Analysis is carried out for all "Variables". Sometimes, these variables number more than 50. In the present case, Tiara encountered more than 20 variables
- Such a Sensitivity Analysis ranks all the Variables in a "Tornado Diagram", showing the variables with maximum impact on top and the variables with less and less impact in a descending order.
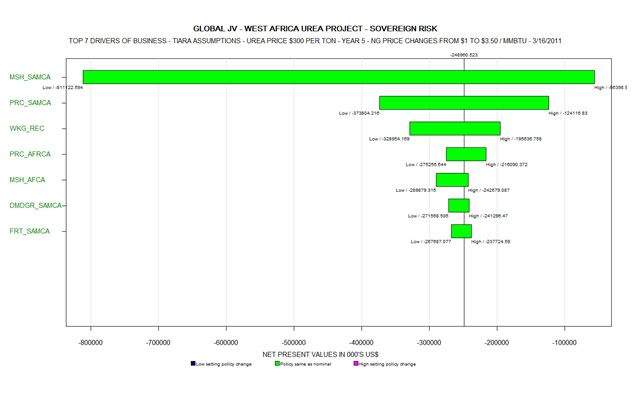
- Thereafter, the top "7 Variables" called "Top Seven Drivers" are projected in a Tornado Diagram as below. These diagrams represent Scenarios 3 & 4 with JV and Tiara assumptions separately for Urea Price at $ 275 and $300 per ton respectively:
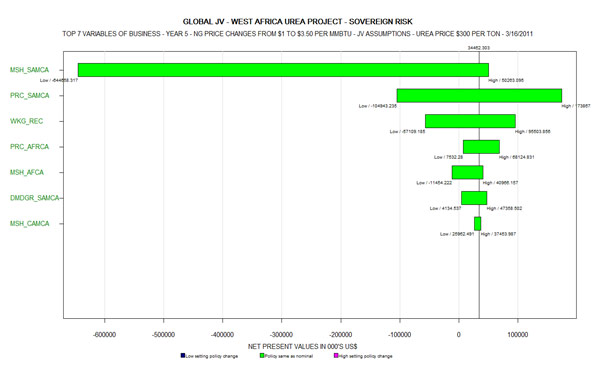
The following are the abbreviations which stand for the variables list:
- MSH - Market Share
- SAMCA - South America
- WKG_REC - Working Capital Receivable
- PRC - Price
- DMDGR - Demand Growth Rate
- CAMCA - Central America
FRT - Freight


These Tornado Diagrams do show what the Principal Drivers are for a given Scenario and a set of Assumptions. Each variable in the Tornado Diagram has "three values", i.e., pessimistic, most likely and optimistic. If two variables are taken together, there could be 9 different and mutually exclusive combinations, i.e., 32. Since there are 7 variables, the number of possible combinations would run at 37, i.e., 2,187 possible mutually exclusive combinations or values. There are two different approaches to carrying this out:
- Monte Carlo Simulation - this would examine roughly around 500 possible combinations for a total number of 2,187 combinations
- Full Enumeration - This will examine all the 2,187 combinations. Since this number is relatively small and the Software that Tiara uses would be able to carry out these iterations in a very short period of time (less than 2 minutes) Tiara carried out full enumeration (2,187 iterations or values) of each of the Scenarios for which the Tornado Diagrams have been drawn.
The Results are shown in the Chart (S-Curves) below:

-
Interpretation of Results in The Form of S-Curves:
There are four curves each representing the following sets of assumptions:
- These curves are drawn, each representing 2,187 Iterations of the scenario under discussion with the Cumulative Probability on the Y-axis and the Net Present Values (NPVs) on the X-Axis.
- The Vertical Lines show the "Expected Values" for the Sovereign Risk Scenario for the JV and Tiara and that too for each of the Urea Price Scenarios, which represent the weighted average (between the probabilities and the NPVs) of each Scenario and the numbers are shown at the bottom. It will be observed that all the NPVs of Expected Values are negative, although for the JV's "Most Likely Scenario", the single point value as per the table was US$ 34.462 million
- The Curves cut the Zero axis (Y-axis) at a specific point. To the left of this point, all the NPVs are negative, whereas to the right of this point, all the NPVs are positive.
- It would also be observed that the curve in "pink color" running at the very bottom, representing JV's assumptions with Sovereign Risk with urea price at $300 per ton intersects the "Zero Axis" at 58%. This would mean that 58% of the NPV's are negative. In the alternative, one could say that the "Probability of Destroying Shareholder Value" in this Scenario is 58%
- All other Scenarios show >90% Probability of Destroying Shareholder Value
-
Lessons Learned from the West African Project:
- Management too often comes up with "gut-feel" in the Decision Making Process. While this is a good exercise in itself since Management carries a lot of "built-in-experience", this contains the very "perceptions, prejudices and biases" that the Management has started with
- It is always good to envision in future Scenarios as to what could go wrong or the "worst" that could affect a company so that the company is prepared for it
- In International Business, it is always good to envision "Sovereign Risks" in future Scenarios. This is particularly relevant for countries in Africa, Asia and South & Central America and the countries in the Former Soviet Union
- One of the major sovereign risks is complete "Nationalization". Even today, it is happening in many countries in Africa and South America.
Decision & Risk Analysis (D&RA), besides envisioning future Scenarios including various Risks involved also has a "Disciplined Environment" to carry out the following:
- Goes into significant granularity of each variable
- Takes into account the pessimistic and optimistic values for each variable
- Provides Probability Distribution of these values for each variable
- Carries out Sensitivity Analysis of "All Variables" in the form of a major Tornado Diagram
- Thereafter, it focuses on the top 7 to 9 Variables or Drivers. If it is top 7 Drivers, the number of possible combinations in the S-Curve for Full Enumeration Option would be 37 , i.e., 2,187 combinations. If one takes top 9 Drivers, then the number of possible combinations would be 39 , i.e., 19,683 combinations. It is possible to carry out such full enumeration in less than 2 minutes with the special software that Tiara carries along with its experience in Quantitative Modeling.
- Runs the S-Curve for each Strategic Option and shows the following:
- The "Expected Values" for each Strategic Option. These are more robust than the single-point values one obtains in a regular quantitative model
- The Risk Profile of the Project with the Probability of enhancing or destroying shareholder value.
-
It is the considered opinion of Tiara that the D&RA with Simulation Exercises should be carried out for every capital investment project involving more than $50 million
This D&RA should be introduced at the conceptual level
11. PRESENTATION TO US-INDIA BUSINESS COUNCIL (USIBC) IN WASHINGTON, DC:
- This Presentation was made to the then President of USIBC
- Highlighted the opportunities for US companies in India, especially with India's Five Year Plan for the Period 2013-18
- Reviewed the flaws in the System of Bidding for Projects by the Private Sector with Government of India (GOI)
- Narrated some of the Problems with Power Generating Companies in India
- Critiqued the Attitudes of some of the Secretaries to GOI
- Discussed in specifics the Opportunities for the Private Sector in the Power Sector
- Offered to assist members of the USIBC for any Market Entry Strategy into India
- Demonstrated Tiara's Quantitative Modeling System
- Ran a simulation Exercise including Monte Carlo Simulation
12. A MAJOR CHEMICALS PROJECT FOR THE SUBSIDIARY IN USA OF A CONGLOMERATE IN INDIA:
- This Project was planned to produce 300,000 tons of Potassium Sulfate (K2SO4) in the State of Utah
- It would call for a total Capex of around $800 million of which $400 million would spent by the end of 2016. The balance would be spent by 2020
- The Market for Potassium Sulfate in the US in 2013 was around 313,000 tons, while the Global Market was of the order of 4.53 million tons
- The US Market was expected to go up to 437 K tons by 2020 while the Global Market would go up to around 7 millions
- As of 2013, there was only one producer in the US (Compass Minerals), who produced 298K tons, more than what the US market needed and was exporting their product. This producer was expected to grow to 350K, 450K and 520K tons in the Years 2013, 2014 and 2015 respectively
- China had the biggest Market Demand with 2.5 million tons p.a., followed by EU with 1 million tons p.a. and Chile with 198K tons. The rest of the world market was fragmented amounting to 767K tons amounting to a total of 4.53 million tons in 2012.
- On an average, this was expected to grow at a CAGR 6% between 2012 and 2020 growing to a level of around 7.1 million tons
- Potassium Sulfate had always a "Premium" over Potassium Chloride in the market place
- However, the Pricing Mechanism collapsed globally with two major players from Russia and Belarus breaking their cartel and the market prices collapsed
- Not only the Premium for K2SO4 was gone, but even banks who were lending heavily to the manufacturers had forecast that the premium pricing was unlikely to recover before 2020
- Meanwhile, two more Manufacturers in the US were endeavoring to enter the global market and they were
- Potash Ridge Blawn Mountain Project in the State of Utah with a manufacturing capacity of 680,000 tons p.a.
- OCOA IC Potash Project in New Mexico with a slated capacity of 600,000 tons p.a.
- Even if only one of the above comes up that would create tremendous competition especially in the US Market which is relatively small at 300K tons p.a. Further, the existing Plant of Compass Minerals will produce by 2017 around 1.5 times the market requirements in the US
- Taking all the above into account, a Quantitative Model was developed together with Scenario Planning and Monte Carlo Simulation. The most likely Scenario had the following results:

The relevant Tornado diagram is as below:

The relevant Risk Profile of the Project and S-Curve is as shown below:
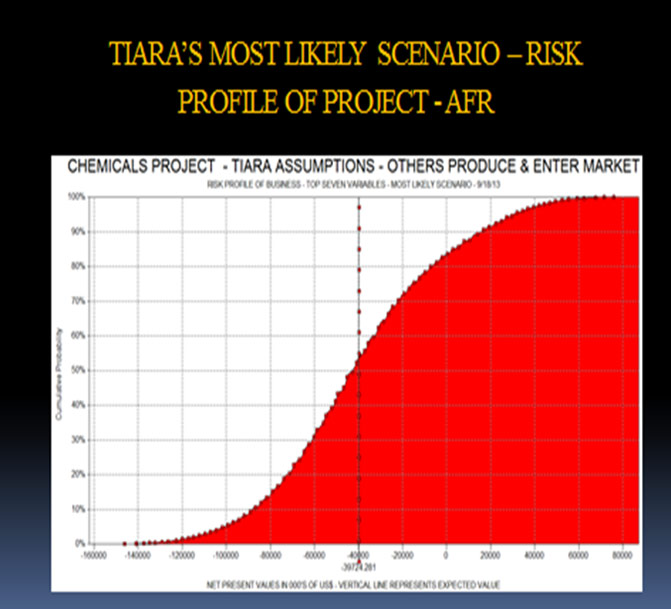
It appears that the new capital investment for a Potassium Sulfate Plant in North America by this company has been abandoned due to the High Risk Profile of the Project
13. BIOGAS PROJECT FOR THE SUBSIDIARY OF A EUROPEAN COMPANY IN INDIA:
- Biogas Production Thru Anaerobic Digestion
- Investigation of various Technologies for Manufacturing Biogas:
- Solid State Stratified Bed (SSB)
- Plug-flow Digester/Reactor (PFDR) Process
- TERI (TEAM) Process
- KVIC Derived Design
- BARC Process
- Continuous Flow Stirred Tank Reactor System (CSTR)
- Upflow Anaerobic Surge Blanket (UASB) System
- Pre-Treatment of feedstocks, where necessary - in the case of wheat and rice straw, pre-treatment is necessary - some kind of pulverizing it
- This is where "Verbio Process" is unique
- "Verbio" Technology:
- Currently uses wheat-straw as the feedstocks
- There is special baling equipment to collect the feedstocks from various farmers quite efficiently
- There is a good storage system as it may be necessary to store 5 months' requirements in the plant storage
- 1,000 tons of wheat-straw plant per day will produce around 16 tons of biomethane per day
- In other words, a 35,000 ton p.a. plant will produce around 5,500 tons of biomethane, equivalent to the rated capacity of a10 MW Plant in power generation
- The feedstocks are well pulverized and treated with special enzymes in the Anaerobic Digestion Process
- This is the most efficient technology yet available for treatment of waste of dung in the manufacture of biogas or biomethane of capacity 10 MW of power
- To produce the same 10 MW of power, 300,000 tons p.a. of cow-dung will be needed
- 200,000 tons p.a. of "kitchen waste" or "vegetable waste" will be needed
- A blend of the above two will need a plant with feedstocks requirements of 250,000 tons per annum
- It should be possible to use rice straw as well in similar capacities to produce same amount of power
- Verbio technology is being currently used by a Plant in Germany to produce 25 MW of power near the Polish Border
- Marketing the Biogas (Biomethane) Output:
- Can be used for Power Generation with a generating set of 10 MW and then feeding the National Power Grid
- Can be used for producing Biomethane for feeding the National Natural Gas Grid in India
- Can be used for auxiliary power generation for an Industrial Plant
- Can be used for producing methanol
- Can be used in place of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) in India and feed the Commercial Segment, which is non-subsidized - this seems to be the logical segment to feed for the following reasons:
- GOI supports this Approach as it conserves the consumption of LPG, 20% of which is imported
- GOI provides "subsidy" for the Capex of the Plant besides various tax concessions
- The pricing of LPG in the commercial segment is significantly higher since it is not subsidized by GOI
- The Project shows excellent "Project Economics"
The Project would need a Capital Investment of around Rs. 60 Crores with the following Results as of the middle of 2014:

The relevant Tornado Diagram, Principal Drivers of the Business, is shown below:

The relevant Risk Profile of the Project is as shown below:
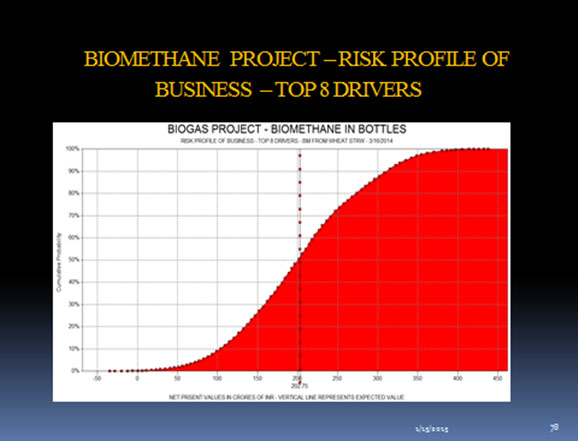
The above curve shows that there is no probability of destroying shareholder value in this project
The relevant Risk Profile of the Project is as shown below:
14. ARRANGEMENT WITH A GERMAN COMPANY, "VERBIO AG" ,TO TRANSFER TECHNOLOGY TO INDIAN COMPANIES INTERESTED IN GENERATING BIOGAS (BIOMETHANE) FROM WHEAT-STRAW (Marketing LPG to the Commercial Segment of LPG comprising of Hotels & Restaurants):
- Generate biomethane (natural gas) from wheat-straw and rice straw; India has surplus wheat- straw of 12 million tons per annum and rice-straw of another 11 million tons p.a. The plant generating 10 MW equivalent power needs only 35,000 tons per annum of wheat or rice straw. Such a Plant will produce around 6,000 tons of biomethane (natural gas or biomethane, i.e., CH4).
- This Technology has been developed in Germany and is the most efficient method of manufacturing biomethane (natural gas) from waste products on a global basis.
- As such the Company undertaking this technology will be ushering in new technology into India
- The German company has a very unique way of "baling" and "wrapping" the wheat-straw with some special equipment. This assists them in baling, wrapping and storing the feedstocks, say 5 months' stocks in their storage area, which would be less than a hectare.
- While in Germany, the biomethane so developed is fed into the gas grid, in India, this can be bottled and sold very profitably in the LPG Commercial Segment
- Provide Biomethane (natural gas) in gas cylinders to the Commercial Segment of LPG. Government of India (GOI) welcomes this and even provides "subsidy" at 10% of Capex as this would reduce their LPG imports, which are in the region of 4 million tons p.a.. Even without including GOI support, this project is exceptionally profitable.
- Generate incremental supplies of fertilizer (organic manure) as a by-product for rural marketing.
- Provide outlet for the wasted wheat-straw and rice-straw in rural areas and in turn put some cash into the farmers' pockets
Given below are the details of the Technology:
-
A German Company has come up with a new unique Technology for the manufacture of Biomethane using "wheat straw" and "rice straw" This is the latest German technology and it has been verified that there is only one German company which uses this technology for producing biomethane and supplying to the compressed natural gas (CNG) grid in Germany. They are prepared to offer this technology to selected companies in India.
- Tiara has already carried out a complete pre-feasibility study on this project and will be happy to present to any Company in India
- The process that is used is "anaerobic digestion", a chemical process
- The technology developed by this German Company is extremely efficient in the use of feed stocks. It needs only 35,000 tons p.a. of feedstocks (approximately 100 tons a day) to produce 10 MW of rated power. To produce this level of power, one needs 237,000 tons of biowaste or around 300,000 tons of cattle dung
.
- The project needs only around 55 crores of rupees as capital investment + some investment on cylinder cascades for storage + sum capex at customers' premises
- This product can easily penetrate the commercial Segment of LPG Market (i.e., restaurants and hotels) where LPG is sold at non-subsidized price.
- While the cost of production is around Rs. 35 per Kg, the revised market selling price can be Rs. 55 per Kg (price to distributors). A downward revision on this price has been made in the light of a drop in International LPG prices recently (Jan, 2015). The non-subsidized LPG price is around Rs. 59 per Kg in India today (this represents the reduced price of LPG with the drop in global prices)
- As such everybody in the distribution channel, i.e., the rural wheat-straw & rice-straw supplier, the manufacturer of biomethane and the Commercial Segment User, will be a winner in this deal
- The cashflows are very robust for such a project and the payback period is in the region 3.5 years and IRR over 37%
The Risk Profile shows that there is a very low probability of destroying shareholder value
- The project also produces fertilizer (organic manure) as a byproduct, which can be sold to the very farmers from whom the biogas manufacturer procures wheat straw and rice straw
Representatives of Tiara have visited the Verbio Plant in Germany near the Polish Border. The slated capacity of this plant is 25 MW of power and it is already producing 10 MW using feedstocks at the rate of 35,000 tons per annum. Incidentally, the plant in India is envisaged with a power capacity of 10 MW.
Tiara would be happy to make a Presentation to any Company that would be interested in ushering in this new technology in India Incidentally, even if a company puts up 6 Plants at different locations in India where, say wheat/rice straw is available (India has a surplus of 12 million tons of wheat straw and 11 million tons rice straw p.a.), the total requirement of feedstocks will be in the region 6 x 35,000 = 210,000 tons p.a. Further, this would achieve a market penetration of LPG Commercial Segment in the region of just 1%. In short, it is a great project with hardly any risk in it and can be implemented by any Company with great aplomb. While GOI provides subsidies in the form of Grants for Capex, Tiara has not included that in our Pre-feasibility Study.
15. MARKET ENTRY STRATEGY FOR A NORTH-AMERICAN COMPANY TO ENTER THE "SUPPLIES TO CLINICAL TRIALS MARKET:
- This was undertaken by Tiara in late 2014
- The Market for Supplies to Clinical Trials Market is huge in North America.
- In US alone, this would be of the order of $4.50 billion per annum
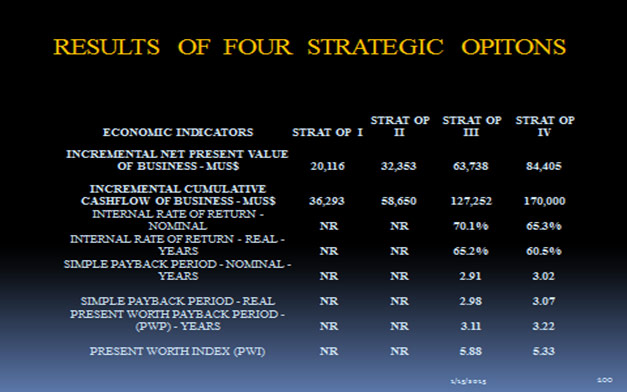
- The following are some of the results of the Study:
- With no Capital Investment and with additional Manpower Resources, the Market can be penetrated with the following results:
The following is the Principal Drivers Analysis Diagram (Tornado Diagram) generated for Strategic Option II:

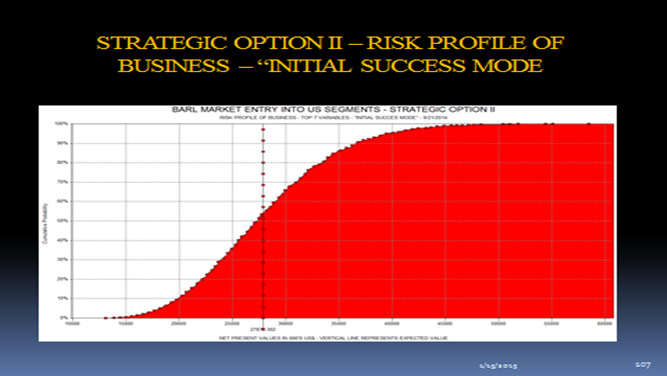
Given below is the Risk Profile (S-Curve) for the Project. This will show that the Probability of destroying shareholder value is nil.
|